31. The Potential of Calcium Phosphate Nanoparticles as Adjuvants and Vaccine Delivery Vehicles
Vaccination is one of the most efficacious and cost-effective ways to protect people from infectious diseases and potentially cancer. The shift in vaccine design from disrupted whole pathogens to subunit antigens has brought attention on to vaccine delivery materials.
30. Tumor Associated Macrophages: Origin, Recruitment, Phenotypic Diversity, and Targeting
The tumor microenvironment (TME) is known to have a strong influence on tumorigenesis, with various components being involved in tumor suppression and tumor growth. A protumorigenic TME is characterized by an increased infiltration of tumor associated macrophages (TAMs), where their presence is strongly associated with tumor progression, therapy resistance, and poor survival rates.

29. Peptide Multimerization as Leads for Therapeutic Development
Multimerization of peptide structures has been a logical evolution in their development as potential therapeutic molecules. The multivalent properties of these assemblies have attracted much attention from researchers in the past and the development of more complex branching dendrimeric structures, with a wide array of biocompatible building blocks is revealing previously unseen properties and activities.
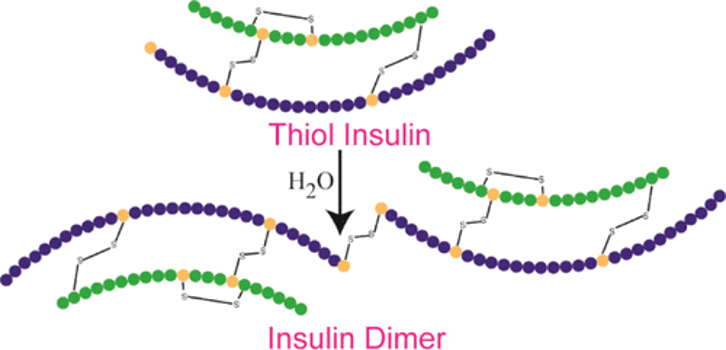
28. Engineering of a Biologically Active Insulin Dimer
The growing epidemic of diabetes means that there is a need for therapies that are more efficacious, safe, and convenient. Here, we report the efficient synthesis of a novel disulfide dimer of human insulin tethered at the N-terminus of its B-chain through placement of a cysteine residue.
![27. [Journal Cover] Cationic Antimicrobial Peptides Are Leading the Way to Combat Oropathogenic Infections](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/642d0cb753153160d6508469/1680842260192-HQT6D4HI7X6FGKW2FBP9/8.5.jpg)
27. [Journal Cover] Cationic Antimicrobial Peptides Are Leading the Way to Combat Oropathogenic Infections
Oral dental infections are one of the most common diseases affecting humans, with caries and periodontal disease having the highest incidence. Caries and periodontal disease arise from infections caused by oral bacterial pathogens.

26. Chemical Synthesis and Characterization of a Nonfibrillating Glycoglucagon
The current commercially available glucagon formulations for the treatment of severe hypoglycemia must be reconstituted immediately prior to use, owing to the susceptibility of glucagon to fibrillation and aggregation in an aqueous solution. This results in the inconvenience of handling, misuse, and wastage of this drug.

25. Retro Diels–Alder Fragmentation of Fulvene–Maleimide Bioconjugates for Mass Spectrometric Detection of Biomolecules
Diels–Alder chemistry is a well-explored avenue for the synthesis of bioactive materials; however, its potential applications have recently expanded following the development of reactions that can be performed in buffered aqueous environments at low temperatures, including fulvene–maleimide [4 + 2] cycloadditions.

24. A Silyl Ether-Protected Building Block for O-GlcNAcylated Peptide Synthesis to Enable One-Pot Acidic Deprotection
In this report, we introduce a novel building block for Fmoc/tBu solid phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) of β-linked O-GlcNAcylated peptides.

23. Pentafulvene–Maleimide Cycloaddition for Bioorthogonal Ligation
The applications of bioconjugation chemistry are rapidly expanding, and the addition of new strategies to the bioconjugation and ligation toolbox will further advance progress in this field. Herein, we present a detailed study of the Diels–Alder cycloaddition (DAC) reaction between pentafulvenes and maleimides in aqueous solutions and investigate the reaction as an emerging bioconjugation strategy.

22. Fluorescent Reporters for Antimicrobial Peptides
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), a part of the natural defence against pathogens, have been considered as alternative antibiotics to combat the increase of antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Given the advanced development of fluorescent probes, extensive research has been focussed on understanding the physiological processes of the interaction between AMPs and bacteria.