
51. Aggregation-Prone Antimicrobial Peptides Target Gram-negative Bacterial Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
Aggregation of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) enhances their efficacy by destabilising the bacterial cell wall, membrane, and cytosolic proteins. Developing aggregation-prone AMPs offers a promising strategy to combat antibiotic resistance, though predicting such AMPs and understanding bacterial responses remain challenging. Octopus bimaculoides, a cephalopod species, lacks known AMP gene families, yet its protein fragments were used to predict AMPs via artificial intelligence tools. Four peptides (Oct-P1, Oct-P2, Oct-P3, and Oct-P4) were identified based on their aggregation propensity. Among them, Oct-P2 reduced the viability of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus by up to 90%, confirmed by confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy. It further aggregated plasmid DNA in vitro, and the presence of extracellular DNA reduced their antibacterial activity. With knockout mutants, it revealed that Oct-P2 was internalised into bacterial cells, possibly through membrane transport proteins, enhancing its antibacterial effect. Aggregation-induced emission assays and molecular dynamics simulations revealed that Oct-P2 aggregates with transcription promoter DNA, inhibiting transcription and translation in vitro. This dual-target mechanism not only highlights the potential of Oct-P2 as a lead template for new antimicrobial drug development, but also opens a new window for discovering AMPs from protein fragments against the upcoming challenge of bacterial infections.

50. Functionalized α-Cyanostilbene Derivatives for Detection of Hypoxia or Proteostasis Imbalance in Live Cells
α-Cyanostilbene represents one of the easily functionalized aggregation-induced emission (AIE) scaffolds. It has been widely adopted for the construction of fluorescent materials for broad applications. Here, we further expanded the utilization of α-cyanostilbene derivatives for the detection of hypoxia or proteostasis imbalance in live cells. Four different amine containing donors were introduced to construct α-cyanostilbene derivatives (R-ASC) with donor-acceptor scaffolds. Equipped with the cysteine (Cys) reactive group, maleimide (MI), R-ASC-MI shows fluorescence turn-on property upon binding with unfolded proteins in vitro and in live cells under proteostatic stress. By virtue of R-ASC-MI, the level of unfolded protein loads in cells can be quantified by flow cytometry, or visualized under microscope. Furthermore, we also characterized the performance of R-ASC-NO2, synthetic precursors of R-ASC-MI, in cellular hypoxia. R-ASC-NO2 revealed upregulated activities of nitroreductase, as well as increased hydrophobicity in live cells, under either chemical (NaN3) induced or atmospheric (1 % O2) hypoxia. Together, the advantages of easy modification and high signal-to-noise ratio of new α-cyanostilbene derivatives reported in this work highlight the great potential of α-cyanostilbene in constructing functional biosensors and many other domains.α-Cyanostilbene represents one of the easily functionalized aggregation-induced emission (AIE) scaffolds. It has been widely adopted for the construction of fluorescent materials for broad applications. Here, we further expanded the utilization of α-cyanostilbene derivatives for the detection of hypoxia or proteostasis imbalance in live cells. Four different amine containing donors were introduced to construct α-cyanostilbene derivatives (R-ASC) with donor-acceptor scaffolds. Equipped with the cysteine (Cys) reactive group, maleimide (MI), R-ASC-MI shows fluorescence turn-on property upon binding with unfolded proteins in vitro and in live cells under proteostatic stress. By virtue of R-ASC-MI, the level of unfolded protein loads in cells can be quantified by flow cytometry, or visualized under microscope. Furthermore, we also characterized the performance of R-ASC-NO2, synthetic precursors of R-ASC-MI, in cellular hypoxia. R-ASC-NO2 revealed upregulated activities of nitroreductase, as well as increased hydrophobicity in live cells, under either chemical (NaN3) induced or atmospheric (1 % O2) hypoxia. Together, the advantages of easy modification and high signal-to-noise ratio of new α-cyanostilbene derivatives reported in this work highlight the great potential of α-cyanostilbene in constructing functional biosensors and many other domains.
49. Dimerization and lysine substitution of melittin have differing effects on bacteria
Introduction: Melittin is a potent antimicrobial peptide from bee venom that is effective against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. However, it is extremely toxic to mammalian cells and, as yet, has no clinical use. Modifications to its amino acid sequence, cyclization, truncation, and dimerization have been attempted in order to reduce its toxicity whilst maintaining its antimicrobial activity.
Methods: In this study, we targeted the three lysine residues present in melittin and substituted them with lysine homologs containing shorter side chains (ornithine, Orn, diaminobutyric acid, Dab, and diaminopropanoic acid, Dap) and made both parallel and antiparallel melittin dimers to observe how lysine substitution and dimerization affects its activity and toxicity. The antibacterial activity of melittin and its analogs was tested against S. aureus (Gram-positive bacteria) and E. coli (Gram-negative bacteria), and cytotoxicity was tested against the mammalian cell lines HEK293 and H4IIE.
Results: Overall, dimerization and lysine substitution exhibited improved antimicrobial activity toward E. coli and limited improvement toward S. aureus. However, mammalian cell toxicity was only marginally reduced compared to native melittin. Interestingly, the parallel dimer was found to be marginally more active than the antiparallel dimer, indicating orientation maybe important for activity, although both dimers were less effective than the native and Lys-analog peptides toward S. aureus. Of the Lys substitutions, Dab and Dap improved melittin’s activity toward E. coli.
Discussion: Dimerization and Lys substitution of melittin improved the antimicrobial activity toward Gram-negative bacteria but did not significantly improve its activity toward Gram-positive bacteria. Some analogs also displayed reduced toxicity toward HEK293 and H4IIE cells but overall remained toxic at bactericidal concentrations. Our data indicates that although highly antibacterial, melittin’s toxicity is the major drawback in its potential use.
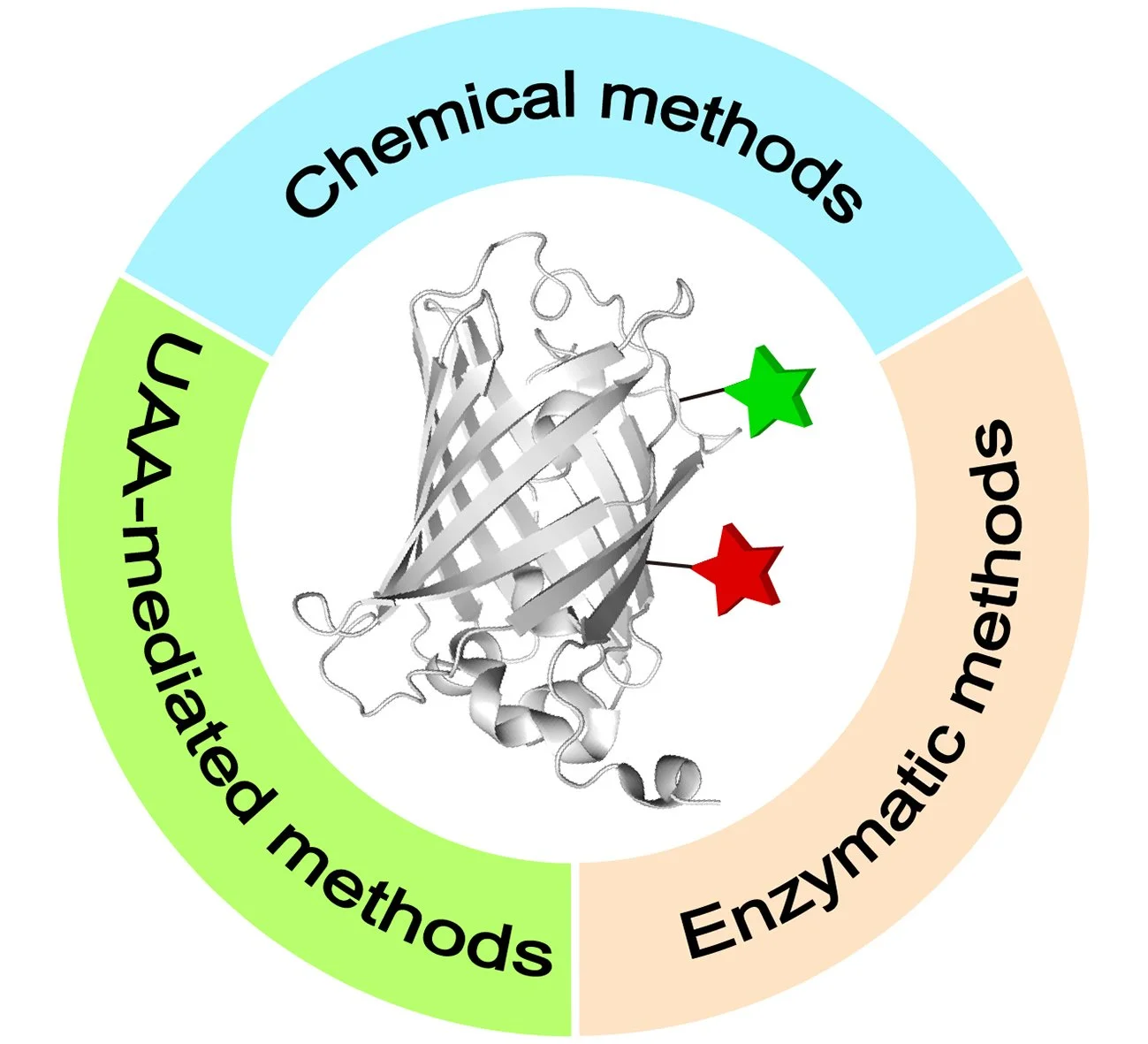
48. Recent Toolboxes for Chemoselective Dual Modifications of Proteins
Site-selective chemical modifications of proteins have emerged as a potent technology in chemical biology, materials science, and medicine, facilitating precise manipulation of proteins with tailored functionalities for basic biology research and developing innovative therapeutics. Compared to traditional recombinant expression methods, one of the prominent advantages of chemical protein modification lies in its capacity to decorate proteins with a wide range of functional moieties, including non-genetically encoded ones, enabling the generation of novel protein conjugates with enhanced or previously unexplored properties. Among these, approaches for dual or multiple protein modifications are increasingly garnering attention, as it has been found that single modifications of proteins are inadequate to meet current demands. Therefore, in light of the rapid developments in this field, this review provides a timely and comprehensive overview of the latest advancements in chemical and biological approaches for protein dual functionalization. It further discusses their advantages, limitations, and potential future directions in this relatively nascent area.
47. Synthetic peptide branched polymers for antibacterial and biomedical applications
The efficiency of traditional antibiotics has been undermined by the proliferation of antibiotic-resistant pathogenic microorganisms, necessitating the pursuit of innovative therapeutic agents. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), which are part of host defence peptides found ubiquitously in nature, exhibiting a wide range of activity towards bacteria, fungi, and viruses, offer a highly promising candidate solution. The efficacy of AMPs can frequently be augmented via alterations to their amino acid sequences or structural adjustments. Given the vast reservoir of marine life forms and their distinctive ecosystems, marine AMPs stand as a burgeoning focal point in the quest for alternative peptide templates extracted from natural sources. Advances in identification and characterization techniques have accelerated the discoveries of marine AMPs, thereby stimulating AMP customization, optimization, and synthesis research endeavours. This review presents an overview of recent discoveries related to the intriguing qualities of marine AMPs. Emphasis will be placed upon post-translational modifications (PTMs) of marine AMPs and how they may impact functionality and potency. Additionally, this review considers ways in which marine PTM might support larger-scale, heterologous AMP manufacturing initiatives, providing insights into translational applications of these important biomolecules.

46. Embracing the era of antimicrobial peptides with marine organisms
The efficiency of traditional antibiotics has been undermined by the proliferation of antibiotic-resistant pathogenic microorganisms, necessitating the pursuit of innovative therapeutic agents. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), which are part of host defence peptides found ubiquitously in nature, exhibiting a wide range of activity towards bacteria, fungi, and viruses, offer a highly promising candidate solution. The efficacy of AMPs can frequently be augmented via alterations to their amino acid sequences or structural adjustments. Given the vast reservoir of marine life forms and their distinctive ecosystems, marine AMPs stand as a burgeoning focal point in the quest for alternative peptide templates extracted from natural sources. Advances in identification and characterization techniques have accelerated the discoveries of marine AMPs, thereby stimulating AMP customization, optimization, and synthesis research endeavours. This review presents an overview of recent discoveries related to the intriguing qualities of marine AMPs. Emphasis will be placed upon post-translational modifications (PTMs) of marine AMPs and how they may impact functionality and potency. Additionally, this review considers ways in which marine PTM might support larger-scale, heterologous AMP manufacturing initiatives, providing insights into translational applications of these important biomolecules.
45. Genome-wide Identification, characterization, and expression analysis of copper-containing amine oxidases (CuAOs) gene family in mangrove Kandelia obovate
Copper-containing amine oxidases (CuAOs) are known to have significant involvement in the process of polyamine catabolism, as well as serving crucial functions in plant development and response to abiotic stress. A genome-wide investigation of the CuAO protein family was previously carried out in sweet orange (Citrus sinensis) and sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.). Six CuAO (KoCuAO1-KoCuAO6) genes were discovered for the first time in the Kandelia obovata (Ko) genome through a genome-wide analysis conducted to better understand the key roles of the CuAO gene family in Kandelia obovata. This study encompassed an investigation into various aspects of gene analysis, including gene characterization and identification, subcellular localization, chromosomal distributions, phylogenetic tree analysis, gene structure analysis, motif analysis, duplication analysis, cis-regulatory element identification, domain and 3D structural variation analysis, as well as expression profiling in leaves under five different treatments of copper (CuCl2). Phylogenetic analysis suggests that these KoCuAOs, like sweet cherry, may be subdivided into three subgroups. Examining the chromosomal location revealed an unequal distribution of the KoCuAO genes across four out of the 18 chromosomes in Kandelia obovata. Six KoCuAO genes have coding regions with 106 and 159 amino acids and exons with 4 and 12 amino acids. Additionally, we discovered that the 2.5 kb upstream promoter region of the KoCuAOs predicted many cis elements linked to phytohormones and stress responses. According to the expression investigations, CuCl2 treatments caused up- and downregulation of all six genes. In conclusion, our work provides a comprehensive overview of the expression pattern and functional variety of the Kandelia obovata CuAO gene family, which will facilitate future functional characterization of each KoCuAO gene.
![44. [Journal Cover] Chemical and Biological Strategies for Profiling Protein–Protein Interactions in Living Cells](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/642d0cb753153160d6508469/1687438711937-MKYPKDCMITDKKE2Z517H/Chemistry+An+Asian+Journal-2023-Cover.jpg)
44. [Journal Cover] Chemical and Biological Strategies for Profiling Protein–Protein Interactions in Living Cells
Protein-protein interactions (PPIs) play critical roles in almost all cellular signal transduction events. Characterization of PPIs without interfering with the functions of intact cells is very important for basic biology study and drug developments. However…

43. Directed chemical dimerisation enhances the antibacterial activity of the antimicrobial peptide MSI-78(4–20)
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is on the rise, leading to 700 000 deaths worldwide in 2020. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are antibiotic agents that are active against multi-drug resistant pathogens and also have a reduced risk of AMR development. Previous studies have shown that dimerisation of the proline-rich antibacterial peptide (PrAMP) Chex1–Arg20 can enhance its antimicrobial activity while also reducing its toxicity. To determine if dimerisation via a simple disulfide bond can similarly improve other classes of AMPs, the α-helical cationic peptide MSI-78(4–20) was used as a model. The monomer alone, an S-carboxamidomethyl-capped N-terminal Cys–MSI-78(4–20) analogue and the disulfide-linked dimer were successfully synthesised and their antimicrobial activity and toxicity were determined. It was shown that dimerisation enhanced antimicrobial activity against the Gram-positive opportunistic pathogen Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213, the Gram-negative bacteria Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 47615. The peptides showed no significant haemolytic activity with red blood cells and only induced 50% lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release in mammalian cells at the highest tested concentration, 15 µM. The MSI-78(4–20) dimer was less cytotoxic than the monomer and S-alkyl monomer. Together, the data support the strategy of AMP chemically directed dimerisation as a means of producing potentially more therapeutically useful antimicrobial agents.
42. Genome-Wide Identification and Bioinformatics Analyses of Host Defense Peptides Snakin/GASA in Mangrove Plants
Host defense peptides (HDPs) are components of plant defensive barriers that resist microbial infection. Members of the Snakin/GASA protein family in plants have functions of regulating plant growth, defense, and bacteriostasis.