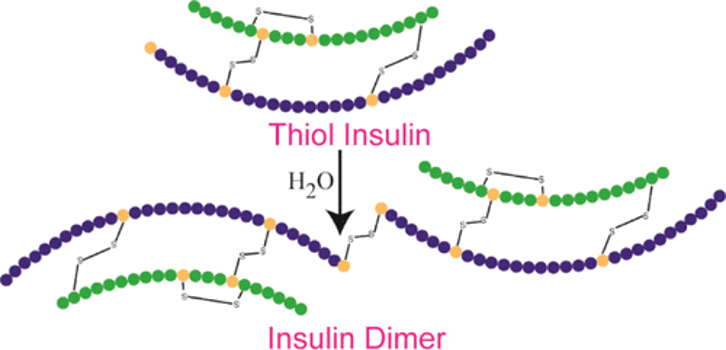
28. Engineering of a Biologically Active Insulin Dimer
The growing epidemic of diabetes means that there is a need for therapies that are more efficacious, safe, and convenient. Here, we report the efficient synthesis of a novel disulfide dimer of human insulin tethered at the N-terminus of its B-chain through placement of a cysteine residue.
![27. [Journal Cover] Cationic Antimicrobial Peptides Are Leading the Way to Combat Oropathogenic Infections](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/642d0cb753153160d6508469/1680842260192-HQT6D4HI7X6FGKW2FBP9/8.5.jpg)
27. [Journal Cover] Cationic Antimicrobial Peptides Are Leading the Way to Combat Oropathogenic Infections
Oral dental infections are one of the most common diseases affecting humans, with caries and periodontal disease having the highest incidence. Caries and periodontal disease arise from infections caused by oral bacterial pathogens.

26. Chemical Synthesis and Characterization of a Nonfibrillating Glycoglucagon
The current commercially available glucagon formulations for the treatment of severe hypoglycemia must be reconstituted immediately prior to use, owing to the susceptibility of glucagon to fibrillation and aggregation in an aqueous solution. This results in the inconvenience of handling, misuse, and wastage of this drug.

25. Retro Diels–Alder Fragmentation of Fulvene–Maleimide Bioconjugates for Mass Spectrometric Detection of Biomolecules
Diels–Alder chemistry is a well-explored avenue for the synthesis of bioactive materials; however, its potential applications have recently expanded following the development of reactions that can be performed in buffered aqueous environments at low temperatures, including fulvene–maleimide [4 + 2] cycloadditions.

24. A Silyl Ether-Protected Building Block for O-GlcNAcylated Peptide Synthesis to Enable One-Pot Acidic Deprotection
In this report, we introduce a novel building block for Fmoc/tBu solid phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) of β-linked O-GlcNAcylated peptides.

23. Pentafulvene–Maleimide Cycloaddition for Bioorthogonal Ligation
The applications of bioconjugation chemistry are rapidly expanding, and the addition of new strategies to the bioconjugation and ligation toolbox will further advance progress in this field. Herein, we present a detailed study of the Diels–Alder cycloaddition (DAC) reaction between pentafulvenes and maleimides in aqueous solutions and investigate the reaction as an emerging bioconjugation strategy.

22. Fluorescent Reporters for Antimicrobial Peptides
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), a part of the natural defence against pathogens, have been considered as alternative antibiotics to combat the increase of antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Given the advanced development of fluorescent probes, extensive research has been focussed on understanding the physiological processes of the interaction between AMPs and bacteria.
21. C-terminus Amidation Influences Biological Activity and Membrane Interaction of Maculatin 1.1
Cationic antimicrobial peptides have been investigated for their potential use in combating infections by targeting the cell membrane of microbes. Their unique chemical structure has been investigated to understand their mode of action and optimize their dose–response by rationale design. One common feature among cationic AMPs is an amidated C-terminus that provides greater stability against in vivo degradation.

20. Recent Applications of Aggregation Induced Emission Probes for Antimicrobial Peptide Studies
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are being intensively investigated as they are considered promising alternatives to antibiotics where their clinical efficacy is dwindling due to the emergence of antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Accompanying with the development of AMPs, a number of fluorescent probes have been developed to facilitate the understanding the modes of action of AMPs.
![19. [Journal Cover] Chemically Modified and Conjugated Antimicrobial Peptides Against Superbugs](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/642d0cb753153160d6508469/1680840739806-W17GF5B1ZWXW8MG3PS13/3.5.jpg)
19. [Journal Cover] Chemically Modified and Conjugated Antimicrobial Peptides Against Superbugs
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is one of the greatest threats to human health that, by 2050, will lead to more deaths from bacterial infections than cancer. New antimicrobial agents, both broad-spectrum and selective, that do not induce AMR are urgently required. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are a novel class of alternatives that possess potent activity against a wide range of Gram-negative and positive bacteria with little or no capacity to induce AMR.